Digital technologies have confidently entered almost all spheres of our lives. There are dozens of mobile healthcare apps in the market, and that is because of the benefits of healthcare mobile app development – the applications help monitor the state of the health and ease the work of medical practitioners and doctors. This article will lift the veil on how such apps are designed and define their advantages for the industry. We will explain the reasons for creating such applications and examine a checklist for choosing a software provider to take over all the technical processes of product delivery. And, we will also shed a little light on the average cost of app development.
Healthcare Mobile App Development Market Outlook
Health apps have become integrated into consumer health informatics as tools that maintain a patient-centered healthcare model by allowing consumers to monitor their health-related problems, understand specific medical conditions and attain personal fitness goals. By means of healthcare mobile app development, doctors and pharmacists can provide safer and more effective care, while patients can self-monitor their treatment and increase adherence to therapy.
Digital Healthcare Industry Components
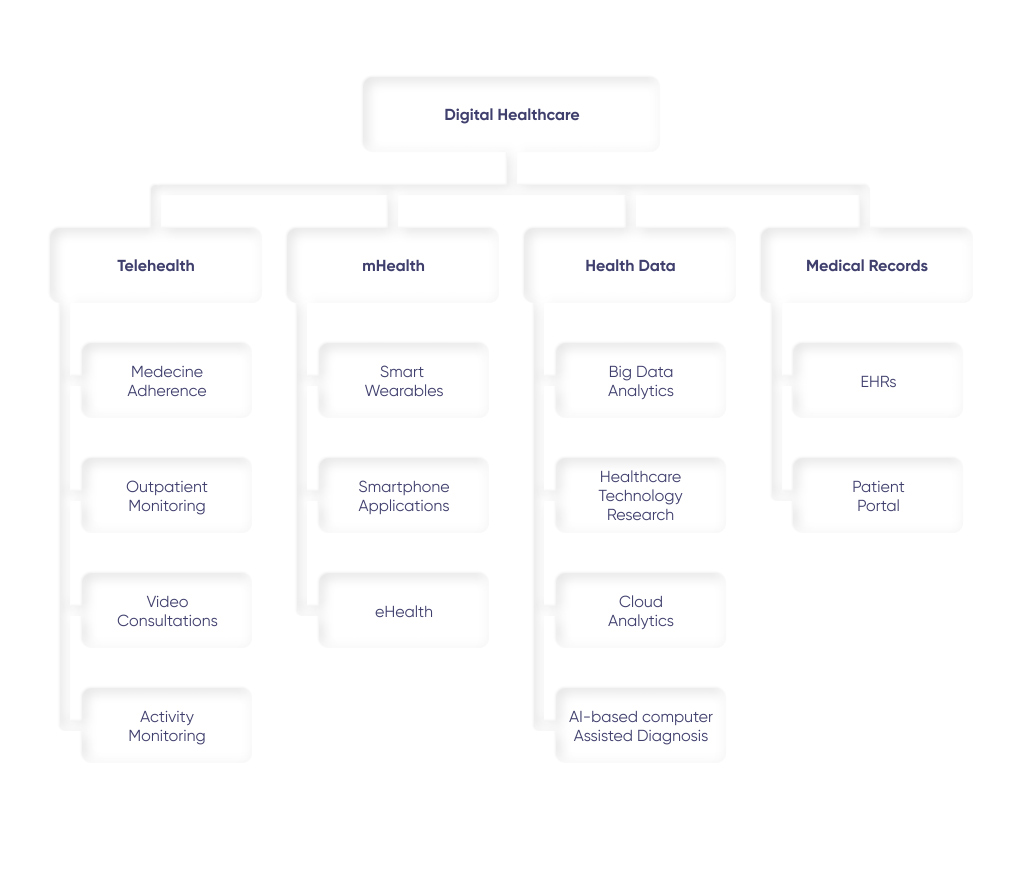
As you can see from the above, the digital healthcare space is quite branchy. It leverages the considerable potential of the latest innovative tech trends, like IoT, Big Data, and AI, for the sake of both patients and healthcare providers.
According to experts, in five years, chatbots will be used by about 80% of clinics and medical institutions. People still want the many benefits of customization, but they are skeptical of the non-transparent methods organizations use to deliver. They want more ownership of their data and of the experience itself. The rise of 5G and augmented reality (AR) put more pressure on leaders to make this a reality. At the same time, emerging technologies have the potential to make experience customization ubiquitous across people's lives. But that future will be unachievable if people continue to feel out of the loop.
Healthcare mobile apps have already rooted in our daily life.
You can find on the market:
- Apps that help users track their biorhythms, monitor sleep, calories, diet, well-being
- Apps that connect patients with trainers, doctors, dietitians, or therapists via online chats saving time spent going to the hospital
- Medication reminders
- Apps that share informative healthcare articles
- Apps that allow users to place an order and then have the needed medication delivered
Impact Of COVID-19 On Global Healthcare
According to Grand View Research, the global mHealth market size was valued at USD 45.7 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.6% from 2021 to 2028. Growing penetration of smartphones & internet connectivity and supportive government initiatives are among the key factors driving the market growth and great demand for healthcare mobile app development. Rising demand for preventive healthcare and increasing funding for the mHealth startups are also expected to boost the market growth. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of mobile health technologies by patients, physicians, and other healthcare faculties is another important factor contributing to the market growth.
The global pandemic has spurred a massive innovation effort from companies, governments, universities, and individuals. Robots are disinfecting cities, cooking hospital food, and delivering packages. Smart devices are monitoring patients' health and collecting valuable health data. Human-AI collaboration is becoming an integral tool for scientists studying the virus. But in this rush to accelerate innovation, it is also vital that organizations think long-term.
Trends in Healthcare Mobile Apps
Down the line, by 2024, the global healthcare app development IT market is forecasted to reach $390.7 billion. Today, the exacerbated concerns about health and the inability to see a doctor encourage people to self-medicate even more. Successful brands can take advantage of this and integrate with DTx (digital therapy) tools. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, virtual reality, big data, and chatbots for pharmaceutical companies are not the future but the trendy present. AI opens for the healthcare sector a sea of opportunities with a number of advantages over clinical decision-making and traditional analytics. Learning algorithms can become more accurate and precise when they interact with training data and allow medical practitioners to gain unprecedented insights, treatment variability, patient outcomes, and diagnostics. Keeping up with digital transformation in healthcare means adapting to the digital era and avoiding outdated business processes.
Trend №1: Consumer Focus In Healthcare
In 2021, we will see a shift in healthcare technology development. In the past, doctors, scientists, and insurance companies have guided technological development to gather the necessary information. We now see the emergence of a patient-centered approach and recognize the importance of the patient experience. How to make life easier for a patient? How can we provide additional value to the user? These questions need answers. So, in 2021, healthcare focus will be on patient experience and improving medicine's effectiveness. We expect a shift towards what we call consumer orientation. Healthcare app developers and providers will use healthcare mobile app development to deliver value-added services and attract more patients, providing more value.
Trend №2: Interoperability
Interoperability in healthcare allows data from multiple health information networks to be shared and accessed by a clinician, lab, or hospital — regardless of the system or application being used and provide the best care possible at any time. It is when hardware and software from disparate systems communicate and exchange data without restrictions. Interoperability occurs at three levels: functional, structural, and semantic.
Trend №3: Telemedicine
In the past, people were reluctant to resort to telemedicine. Now many people understand that it is fast, convenient and high-quality. It was with the advent of the pandemic that the full potential of this technology was revealed. It is useful not only for patients but also for medical professionals. All major scientific conferences have moved online. Such measures used to be exclusively face-to-face, but there has been a forced displacement.
Trend №4: Integration with medical equipment
The integration of telemedicine platforms with equipment is helpful in several cases. The application will help you connect multiple medical devices to gather real-time patient readings and correlate and interpret those results, or you can develop an API for remote access to devices that will assist in tracking the vital signs of patients.
There is always room for development apps to integrate with:
- electrocardiographs
- pacemakers
- automatic tonometers
- sugar level sensors, etc.
Trend №5: Virtual Waiting Room
Another major trend in healthcare mobile app development is likely to be the creation of a virtual waiting room to avoid the risk of infection in a physical waiting room amidst the pandemic. The technology will create a virtual waiting room, possibly in the form of a smartphone app, through which patients can receive notifications when they enter the building. A virtual waiting room is a process in which a patient can check in from their mobile device and remain in their vehicle until an exam room is available. It allows the patient to bypass the traditional waiting room, minimizing the risks of exposure to other patients and germs and viruses present on surfaces, shared devices like kiosks, and materials like magazines, books, papers, clipboards, and pens. Even after the pandemic is over, such an approach can assist doctors and staff in the workflow and help people avoid unnecessary contact. Many companies are now expanding the functionality of their products by adding a virtual waiting room.
Trend №6: Remote Monitoring Of Elderly Patients
The world's population is aging rapidly due to a combination of low fertility and increased life expectancy. According to the World Health Organization, in 2020, there were an estimated 727 million persons aged 65 years or over worldwide. This number is forecasted to double by 2050, reaching over 1.5 billion persons. The share of older persons in the global population is expected to increase from 9.3% in 2020 to 16.0% in 2050, and by 2030 the population over 60 years old will grow to 1.4 billion.
Such a large number of older people means higher costs for medical care. With the growing number of seniors and the added pressure of COVID-19, we need to find better ways to care for older people. WHO has developed a digital health technology tool (WHO ICOPE Handbook App) that helps healthcare providers improve older people's care. This set of technologies provides monitoring elderly or chronically ill patients at home, allowing high-risk patients to avoid potentially hazardous hospital visits. If something goes wrong, the app can provide a faster way for the doctor to interact with the patient. Physicians won't need to monitor patients 24/7 as the app will control the patient's condition via wearable devices and alert them and their caregivers if needed.
In 2021, remote patient monitoring will continue to improve. We will see this type of healthcare mobile app development skyrocket and even more tools to be developed to help provide care. Apps can help with medications and appointment notification, and chatbots and other digital devices can support healthy aging.
Trend №7: Supplemented Intelligence To Support Clinical Decision Making
Science companies are using artificial intelligence to discover and develop new drugs and vaccines. There are many healthcare opportunities for the use of AI, particularly in clinical decision-making, to help doctors diagnose diseases. It is probably one of the most extensive areas where we will see AI evolve in 2021. Artificial intelligence will help calculate the likelihood of certain conditions, but the decision will ultimately lay on the doctor. ML-based diagnostic systems have become more accepted. Future AI/ML tools will help support or protect patients who may need assistance before emergency conditions occur. For example, patients who forget to take their medicine or take them at the wrong time or in undesirable combinations could be prioritized for nurse visits or calls or counseling and education during routine visits.
Types of Healthcare Mobile Apps And Their Functions

The type of application affects the whole healthcare mobile app development process. Precisely, the product's functionality, integrations, and the required level of data security. Mobile health apps depending on their purpose of use, can be divided into apps for consumers (general public) and apps for health professionals and medical facilities. Let's overview some of the most popular mHealth apps.
№1: Fitness apps
Due to the Covid-19 pandemic, many fitness centers around the world have been temporarily closed. Experts immediately noticed a surge in the popularity of home workout apps. These apps help people keep track of their health and fitness by providing different training programs without spending much; therefore, they are trendy. By the way, we created nine recommendations on building a fitness app.
Features:
- Quick & effective workouts from celebrity trainers
- Setting and reaching goals with customized workout plans
- Browsing by workout category, body part, length, and intensity
- Training on-demand/join an upcoming class
- Guidance
- Integration with real-time heart rate using HealthKit + Apple Watch/Samsung Watch/others
Examples: 8fit, FitOn, Fit Radio
№2: Telepharmacy or Drug Dispensing Applications
Staying healthy and getting your medications exactly when your body needs them is vital, but sometimes you just forget. Physicians use it to calculate individual drug doses based on the patient's current condition, age, weight, and other personal information while avoiding time-consuming manual calculations, spreadsheets, and complex tools.
Healthcare application development can help manage a user's medication, track their disease, establish healthy habits and share data with doctors and caregivers. Advanced AI and machine learning can be used to facilitate personalization and enable proactive, preventative interventions.
Useful functions:
- Integration with electronic health records, where the doctor can keep records of the patient's condition, treatment history, medications, and dosage.
- Setting reminders by the attending physician for patients not to forget about taking medications (names of drugs and dosage).
- Dose optimization based on clinically validated pharmacokinetic models, patient’s characteristics, drug concentrations, and genotype.
- Predicting treatment outcomes.
- Charts with progress overview.
- Making reports and sharing them with the doctor.
№3: Risk Assessment Applications
Monitor patients' health in real-time through integration with the EHR and other health monitoring devices that users wear. A good example of risk assessment healthcare application development is the FHR 5-Tier app for obstetricians, midwives, and nurses who use Electronic Fetal Monitoring (EFM) for women in labor.
Useful features:
- Interpretation of fetal heart rate (FHR) recording to aid in real-time patient care decisions.
- Automatic notification of doctors if monitoring devices have identified a threat to the patient's health (mother and/or fetus).
Examples: Ada (a fast AI-powered symptom checker), Symptomatic (an advanced symptom checker with AI to evaluate symptoms)
№4: Mobile health apps for patient-doctor communication
This is one of the most sought-after types of healthcare mobile app development. Such apps can help users to find a medical specialist, make an appointment, arrange a video call, and pay for a consultation through an integrated payment gateway. Such services can increase patients' involvement in the treatment process and enhance their loyalty to the healthcare provider, providing greater transparency between clinicians and patients. A typical mobile on-demand app for doctors can include the following features:
- Built-in messaging system
- EHR
- Search for drugs, prescriptions
- Virtual waiting room, two-way video communication
- 1-to-1 chat
- Video/Audio Call
- Conferencing
- HIPAA Compliance
- Health Report Sharing
- Telemedicine
Examples: MirrorFly, Siilo, HealthTap, Ease, Visit
№5: Diet and Nutrition Applications
It was revealed that obesity-related diseases are among the top three killers in most countries for the last few years. Overweight/obesity is a problem of wide concern that is potentially treatable/preventable through mHealth. There are a dime a dozen of such applications on the market. The standard diet app suite includes nutritional (diet) recommendations, an extensive library of recipes and food descriptions, a calorie counter, diary, and progress chart. Check our article to find more about the development of diet and nutrition apps.
Features users like:
- Lightning-fast food logging
- Foods mega-database validated and updated daily, with restaurants, grocery stores, special diets, and ethnic foods
- AR Grocery Check tool for wiser, healthier shopping (to identify the location of a shopper inside a store and guide through the shopping experience)
- Track nutrients
- 370,000+ recipes database
- Shopping list
- Customizable dashboard for what's important to you
- Plan a user's meal and track carbs, fats, proteins, and total calorie intake.
- Built-in barcode scanner for information on nutrients in food in stores.
- Registering food images in the app
Examples: MyFitnessPal, MyNetDiary
№6: Disease control and monitoring applications
Such apps are in high demand these days. Disease tracking apps are used to reduce the number of people infected with Covid-19. There are also apps for patients with memory impairments that help users with epilepsy, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, asthma, allergies, and even depression monitor their diet and medication and predict their health.
Feel free to check our detailed overview of building a disease control app.
The healthcare app development process, in this case, can include adding the following features:
- Manually enter seizure information so that the user can specify the type of seizure, time of day, duration, and other related information.
- Smartphone video recording, so users can describe to the doctor (or family) their seizures, their triggers, and what happened after.
- Self-management tools: Patients can measure their blood pressure or heart rate anytime they want to and save the result.
- Notifications and reminders: To remind the patient to schedule a consultation, take his pills, go for a walk, or get a blood test.
- Medication list and schedule: Chronic care coordination apps with a calendar are necessary for the patients to keep track of their pills and avoid skipping pills or overdosing.
- Patient data summary reports: Health data reports are required for the doctor to analyze the changes over time and make adjustments to the treatment program.
- Interactive guidance: This is a telemedicine feature that allows a patient to schedule a video consultation with a doctor.
- Real-time feedback and chat: With this feature, a patient can immediately contact a doctor if he/she feels sick.
Examples: Covid Symptom Study app, Carezone, Instant Heart Rate app, COVID Tracker
№7: Lifestyle apps
Some may wonder if lifestyle apps even belong to healthcare app development. But they truly are a part of the healthcare industry umbrella offering a mixture of daily advice with exercises, training, or courses to improve the overall state of mind and well-being.
If we can order takeaways and taxis at a tap of a button, why not meditation sessions too? With increased stress and the need for multitasking almost everywhere, there is a thriving demand for lifestyle apps.
Features you may consider adding to your app:
- Social integration
- Access from any device
- Reminders & push-notifications (drink water, go to bed according to the schedule, stay active and do some exercises)
- Meditation sessions
- Goal setting
- Progress tracking
- Daily advice
- Connection to wearable devices like Apple Watch/Samsung Watch/Fitbit & ability to use as a standalone app
- Fitness coaching
Examples: Calm, Fabulous, Stoic
№8: Apps for social networking and health forums
Community is also important, especially in the state of the pandemic. To stay on top of the latest digital trends in healthcare, there are social networking sites for medical professionals to interact, learn and share their knowledge.
Features you may consider valuable while working on social networking healthcare application development:
- Video Calls
- Voice Calls
- Voicemail
- Notifications
- History log/calls
- HIPAA Security
Examples: Doximity, DailyRounds
№9: Assistants for pregnant
It presents a comprehensive tool for pregnant women. Some features include a pregnancy newsfeed, exercise and nutrition tips, and a daily maternity calendar. The app also has a birth plan checklist, a contraction timer, and a baby names finder. Once the baby is born, the app will transition into a daily parenting guide.
Features you can be inspired by for your app:
- Fertility Tracking, Pregnancy, and Labor Features
- Ovulation Calculator & Calendar
- Articles and advice about preparing to get pregnant and trying to conceive
- Baby Due Date Calculator
- Bumpie Photo Diary, a simple pregnancy photo tool to capture weekly belly pics and turn them into a time-lapse bumper video to share or keep in a pregnancy journal
- Contraction Timer
- Baby Kick Counter
- Baby Registry Checklist
- Pregnancy Calendar with hundreds of informative BabyCenter articles
- Baby Names Finder, a place to search for names you might like by meaning, origin, theme, and more
Examples: Pregnancy tracker , Flo
Healthcare mobile app development services cost
 The more complex the concept is, the more expensive healthcare application development is. Custom UI elements, the number of screens and application states, buttons, fields, business logic, and the server infrastructure require many hours of development and subsequent testing.
The more complex the concept is, the more expensive healthcare application development is. Custom UI elements, the number of screens and application states, buttons, fields, business logic, and the server infrastructure require many hours of development and subsequent testing.
The healthcare mobile app development cost usually depends on:
- Pre-development (analyzing the competition, market stage, identifying features for implementation, etc.)
- Number of platforms that you are going to target (iOS, watchOS, iPadOS, Android, Wear OS, or both)
- Use of some specific technology and innovations such as Machine Learning, AI, etc.
- The complexity of app design, customizations, branding, animations, etc.
- Software development vendor you choose to work with.
Screens, actions, and data in the app. This part is considered one of the most expensive. Each screen must be thought of:
- Choose the optimal arrangement of elements and buttons.
- Think over the business logic.
- Take care of the user's convenience.
Behind this lie hundreds of hours of different specialists – from the project manager to the tester.
According to Research2Guidance research, which analyzed 2,400 mobile healthcare providers, the average cost of healthcare application development is approximately $425,000. Only 47% goes directly to development. The rest is marketing, licensing, administrative costs, etc. Thus, about 36% of all suppliers spent less than $25,000 on developing their mobile applications, while only 12% had a budget exceeding $500,000. At the same time, the chances of success correlate with the size of the budget: the larger it is, the greater the likelihood of success.
The table below illustrates the range of costs to build an app with a timeline accordingly:
| Basic App (core feature set, 1 platform) | Full Product (more features and more complex design, 1 platform) | Large App (complex app design, development, and support, 2+ platforms) | |
| Total cost | ~$35,000-$100,000 | ~$100,000 -$150,000+ | $150,000+ |
| Timeline | ~3-5 months | ~4-9 months | 9+ months |
Why do you need a healthcare app?
eHealth applications are usually created for two reasons: to make money and/or to improve the quality of medical services provided. The first reason is essential for business people who tend to launch relatively simple fitness apps, insurance, or consulting apps to enter a market that will reach $50 billion by 2050. The technology makes it easier to monitor vital health parameters and provides much-needed convenience, so patients are more than willing to use these apps.
The stats really speak for themselves:
- Global Mobile Health (mHealth) Market Forecasts to 2023 by Type of Service, Device, Stakeholder, and Geography – CAGR Expected to Grow at 25%
- 79% of patients will prefer healthcare providers who use digital solutions to reduce time spent on bureaucracy and increase doctors' time with patients. Eight out of ten patients say that hospital visits have become more efficient with broader use of information management technologies, and hospitals' admissions and discharges are much faster.
- According to the Boston Technology Corporation, 74% of patients say using mobile apps and other tools helps them cope and manage their illnesses.
Benefits of healthcare app: for the business owner, for the user
Healthcare application development is beneficial for everyone. For the patient it means obtaining medical care, for the specialist – the workload of routine operations is reduced and allows more time to be devoted to the actual diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. Moreover, mobile access to information makes it easier to obtain data, speeds up decision-making, and reduces patient and doctor distance.
What are the benefits for the user:
- Enhanced communication and feedbacks
- Faster access to providers and care Improved medication adherence
- Remote patient monitoring possible and easy
- Increased medication reconciliation accuracy, which improves patient’s safety
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle
Benefits for the business:
- Increased customer loyalty
- Increased engagement by building a closer relationship with customers
- Automatization of tasks
- Attracting customers
- The app can improve or even save people's lives
Things To Consider Before Developing A Healthcare App

№1: Select Mobile Platform
When you’ve already formulated your future app's concept, it is worth thinking about the application platform. Android and iOS development have their own characteristics. Choosing a platform for healthcare mobile app development is a key stage in a business plan when designing a mobile app because the budget, audience coverage, the specifics of healthcare app development, and marketing of your future application depend on it.
After you have decided on the app idea, functionality, and OS platforms, you need to draw up competent technical specifications to describe the application's functions, components, use cases, etc. It is unnecessary to write specifications using the "technical language" to outline its main features and ideas. A healthcare app development company will take care of the implementation. If you do not have programming and web design skills, then you will need to find a reliable development team to create an application.
By the way, the iOS-based mHealth apps are projected to exhibit a robust CAGR of more than 40.0% from 2020 to 2027, according to the research. This considerable growth of the segment is attributable to the rising adoption of Apple smartphones.
№2: Define Your Target Audience
For the application to accurately find its users, you need to determine its precise target audience. A custom portrait includes demographic, social, and other characteristics with a potential user's specific goals.
When creating a buyer persona, you must answer the following questions:
- What problem will the application solve?
- Who will use it and why?
- What makes the app unique (how it differs from the competitor)
- Who will use it? (age category) and what characteristics (gender, age, education) distinguish this audience?
- Are there ready-made, similar to yours, successful solutions on the market?
Focus on one problem that will be solved with the advent of the application, and not all at once.
Don't try to create an all-in-one app with many functions:
- Plan functionality and design around users' needs and preferences
- Use the best monetization model
- Develop a precise and effective marketing campaign
- Define the type of the app: patient-oriented/doctor-oriented
- Determine the healthcare application development goal: internal use/monetization
№3: Select monetization model
There's no point in building an app just for the sake of it. Think of profit. (Yours and your clients'.)
Registration Fee and Subscription Model
Registration and subscription fees are some of the most common ways of making money from apps. It works best for aggregators where medical practitioners, wellness experts, hospitals, etc., can pay and register for users to find them. Similarly, users may also have to pay a minimum subscription fee to avail the details.
Premium Content + Freemium
Derived as the combination of the words 'free' and 'premium,' the freemium model is one of the most popular app monetization strategies. If functions on the premise of adding value to users. Users get to download the app for free, use a trial version and then upgrade. This is perceived as fair, as users have an idea of what's on offer and what they are paying for.
In-App Purchases and Merchandising Model
This model works best for health apps with gamification attached to it, where users can buy credits to power up or get extra lives. This also extends to paying upfront (i.e., through the app) for an appointment or consultation, etc.
In-App Ads
One of the most popular ways of making money on the app, the in-app ads model allows apps to allow external brands to advertise on their apps for a fee. Like television and radio advertisements, brands can pay app companies to display their products/service ads.
№4: Comply With Data Security Requirements

Suppose you are planning to develop a professional mobile application that handles sensitive patient data. In that case, you should consider the laws and safety regulations that govern this market in the country of your choice. Without this, your application cannot be marketed in such marketplaces as the Google Play Store and App Store, and this can also lead to lawsuits from users and governments.
Compliance with legal and safety regulations
Safe storage of personal health data is vital for healthcare app development. Disclosure of this information is considered a severe violation of the law. Besides, it can harm patients whose safety has not been ensured. The storage and processing of data in the healthcare sector are carried out following strictly regulated rules. Your future application must comply with international and national privacy requirements that determine the rules for working with medical data: HIPAA, PHI, HITECH (USA), GDPR, DPLEF, DPLED (The European Union), The Data Protection Act (The United Kingdom, PIPEDA (Canada) and others. Let's overview these regulations a bit closer.
Who are data controllers and data processors in healthcare app development outsourcing?
The data controller is the person or company that determines the conditions for data processing. In software development, it's a client. A data processor is a person or company that processes data on behalf of a controller according to the controller's instructions. In outsourcing, it's a contractor.
Protected Health Information (PHI) is your/my/everyone's healthcare data. PHI is the content that HIPAA tries to protect and keep private. The Safe Harbor Rule identifies what kind of data you must remove to declassify PHI. Covered entities are individuals in a healthcare field that use and have access to PHI. They are doctors, nurses, and insurance companies. Business associates are individuals that work with a covered entity in a non-healthcare capacity and are also responsible for maintaining HIPAA compliance as covered entities. Lawyers, accountants, administrators, and IT personnel that work in the healthcare industry and have access to PHI are some common examples of business associates.
HIPAA The HIPAA Privacy Rule is the foundational piece that all applicable organizations need to familiarize themselves with. The Privacy rule explains when and how authorized personnel can access PHI. This includes healthcare professionals, administrators, lawyers, or anyone else within your health information ecosystem. That's why the first step towards HIPAA compliance is familiarizing yourself with the Privacy Rule.
ADA (The Americans with Disabilities Act) is another act that you must consider when creating an app that describes the prohibition of discrimination of people with disabilities and ensures that companies have accessibility standards. It also concerns medical applications. For instance, you need to comply with ADA when building an inclusive social media platform.
GDPR The purpose of the GDPR is to protect individuals in connection with the processing of their personal data. This Regulation applies to those who may store such data within the EU/EEA and those outside the EU/EEA who may offer goods or services to individuals in this field or send personal data to organizations within the EU/EEA, or send personal data to recipients within the EU/EEA. We hope that shortly the legislation will relieve us of personal data protection problems and effectively protect our information. Until then, the right to information security rests more on to whom this or that information concerns and requires their initiative and direct participation in privacy.
DPA Data Protection Act (UK legislation) applies to 'personal data,' which relates to individuals. It gives individuals the right to access their own personal data through subject access requests and contains rules which must be followed when personal data is processed.
PIPEDA has a lot in common with GDPR. On 17 November 2020, the Digital Charter Implementation Act (DCIA) was introduced by the Canadian Minister of Information, Science, and Economic Development. Should it be passed, the DCIA will replace Canada's current data protection law for the private sector, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA).
PIPEDA does not require perfect safeguards that eliminate all personal information security risks transferred to a service provider. Organizations that outsource the processing and storage of personal information should be mindful of that potential difficulty and make informed risk-based business decisions about establishing and maintaining their outsourcing arrangements.
№5: Select Primary and Secondary Features
 You need to prioritize appropriately. It means that in no case should you
skimp on user experience design, security, and tests. On the other hand, even if you have an unlimited budget, you can reduce the number of features and not go broke on expensive technologies when launching the app. For example, it makes no sense
for startups to create a native application. Now, cross-platform healthcare app development has increased significantly, so users will not even see the difference. Critical features are only necessary when launching the app to some initial test users, putting the
primary app features into action.
You need to prioritize appropriately. It means that in no case should you
skimp on user experience design, security, and tests. On the other hand, even if you have an unlimited budget, you can reduce the number of features and not go broke on expensive technologies when launching the app. For example, it makes no sense
for startups to create a native application. Now, cross-platform healthcare app development has increased significantly, so users will not even see the difference. Critical features are only necessary when launching the app to some initial test users, putting the
primary app features into action.
Here are the questions that will help you to define critical or absolutely necessary:
- What are my app's killer features?
- What is the ultimate value my app brings?
- Does this feature solve the user's most important problem?
- Is this feature something you should save as a premium feature for later monetization?
- Does this feature support an initial objective or a future objective?
- Is this a nice to have feature?
- Is this merely a cool feature but not the core feature?
Personalization, customization, and other essential features
- Security, Privacy, Data Encryption, multi-factor authentication.
- Accessibility for people with disabilities (text-to-speech or speech-to-text apps, support for larger fonts, augmentative communication software, sign language translators, and others.)
- Tracking — to monitor the state of health either by a person or by their physician.
- Scheduling — to make appointments and by doctors to manage them.
- Push notifications and reminders.
- Payments — to pay for medical services.
- Integration with wearables such as Apple Watch, Fitbit, or Garmin.
- Personal doc's/patient's account to receive messages and notifications and have access to the state of patient's health all in one place.
- Telemedicine options for remote diagnosing in real-time text/video chat to help patients connect with doctors in case of emergency or discuss diagnoses or treatments.
- Security and privacy. Users expect the security level to be on par with financial apps.
- Reporting and charting functions.
- Social integration and networking.
№6: Select The Tech Stack For Your App
Think holistically about which software technologies are starting to fade out and which grow in adoption or are mature with a good ecosystem and strong proof points. You don't want to choose a tech stack that is so novel that it poses risks. Lean toward something that has been deemed "tried-and-true" and is trustworthy. However, this doesn't mean you have to go with some old legacy technology. There are great options out there for mature frameworks and technologies that are trending and have a vibrant development community.
To develop different healthcare software types like:
- Electronic health record (EHR) software
- Hospital management software (different CRMs and more)
- E-prescription software
- Imaging and visualization software
- Diagnostics and therapeutic software
- Embedded medical devices and medical equipment management
- Urgent care applications
- Medical billing
and more, in 2021, the following technologies are used:
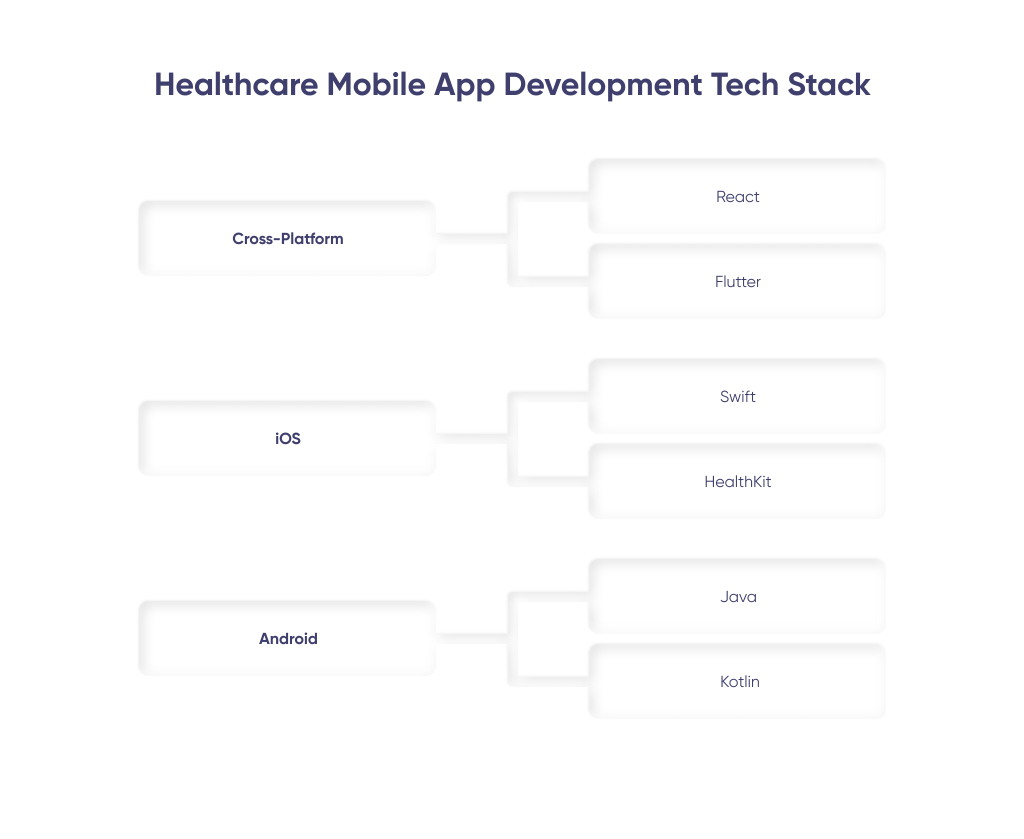
Cross-platform: It is less costly and allows faster healthcare app development due to the single code base. Here, Xamarin, or the classic rivals React or Flutter, will come to the aid. With React, healthcare app development gets better productivity.
Ongoing faster rendering and its data binding structuring enhance the code stability. Both React and Flutter allow for the same code-reusability for Android and iOS. Flutter's widget services and ease of development contribute to a better healthcare mobile app performance.
Android: Kotlin is today prevalently used for Android healthcare mobile application development. It is lightweight and less cumbersome compared to Java. At the same time, it is fully compatible with Java Virtual Machine and allows us to use both frameworks for developing the app.
Java: Today, Java is still considered to be the most popular language for Android apps, though it is mostly used to support previous versions of apps. It has a huge variety of built-in Java libraries to quickly and efficiently develop applications for the above-mentioned OS.
IDEs: Android Studio and Android Developer Tools (ADT) are just great tools to develop Android apps.
UI: For the user interface, it is commonly used Android UI and Jetpack Compose.
iOS: Objective-C is an Apple-supported language used for building iOS applications. It offers object-oriented potential and a productive runtime environment. It is more stable and provides easier usage of private APIs. But because of its complexity, more developers prefer to use Swift. Swift provides a rapid development process and enables improved safety and performance, but it has poor interoperability with third-party tools and IDEs. That's why it is mostly used for supporting previous versions of apps.
IDE: Most developers prefer Xcode, or, less often, Appcode IDE (powered by third-party.)
UI: For building user interfaces, mobile developers commonly use UIKit and SwiftUI. You can also consider integrating with HealthKit when designing a healthcare app.
№7: Build An MVP
Depending on the project, the minimum viable product leads to a significant reduction in time-to-market – sometimes even up to 10 times! The MVP launch allows us to offer users the first version of their mobile application much earlier than if the development was carried out at once for all the intended functions.
Using cross-platform frameworks
Mobile app development starting from MVP can occur natively for specific platforms – for example, iOS and Android – or based on a universal framework. Using Flutter or React Native, you can create one application that will work on all platforms at once. Thus, at least half of the development time is reduced, and any changes and improvements are reflected in versions for all platforms. The disadvantages of this approach are the increased application size and imperceptible performance degradation for the user. But for business projects, time-to-market is often much more critical.
№8: Test Your App And Don’t Be Afraid Of Bugs
Most IT teams work hard before release, although it is more rational to conserve energy. Teams will need to quickly fix bugs that will surely come out after the app's release. First, there is no need to be afraid of some issues at this stage: a quick reaction from devs and technical support can turn even the most fierce critic into a loyal user.
Second, remember that bugs in the application are expected, and errors in user data are unacceptable. That being said, ensuring user privacy doesn't have to stretch the launch timeline: there are simple yet reliable techniques to ensure that legal requirements are met.
Third, remember about Unit testing. It may seem like a tiresome process at first, but in the long run, its benefits are clear. Unit testing ensures that all code meets quality standards before it's deployed. This provides a stable engineering environment where quality is paramount. Throughout the product development life cycle, unit testing saves time and money and helps developers write better code more efficiently.
This is an excellent topic because we're only just seeing the tip of the iceberg in terms of how we can apply digital solutions to healthcare. However, when I say that, I also want to emphasize that it's vital not to be too digital. I mean that you cannot and should not replace good healthcare professionals with IT. What you can do is make digital systems that will support them and make their work more efficient.
Why Healthcare Startups Fail
 There are more than 370,000 health-related apps available on both App Store and Play Market. In
the life of any startup, there are plenty of opportunities for missteps. And pivoting isn't as easy as for companies developing tech solutions, like a photo-sharing app. Mistakes in a healthcare startup can be fatal.
There are more than 370,000 health-related apps available on both App Store and Play Market. In
the life of any startup, there are plenty of opportunities for missteps. And pivoting isn't as easy as for companies developing tech solutions, like a photo-sharing app. Mistakes in a healthcare startup can be fatal.
№1: A Lack Of UX Design Simplicity and Accessibility
A well-thought-out interface helps to quickly and easily establish communication between a medical professional and a patient, saving their time by optimizing data storage and usability. It is crucial to establish interaction between the visible part of the application (frontend) and its invisible part (backend.) That is why medical applications need to have well-placed labels for quick, easy navigation and balanced, calm color palettes.
According to statistics, the user will make a maximum of three attempts to understand the app. If one fails to register, make an appointment with a doctor, or get a recommendation, the app will most likely go to the trash. It must be borne in mind that among the users of medical applications, there are millennials and people aged 40+ and 50+. However, even if your service is aimed at such an audience, this is not a reason to design in the style of the early 2000s.
As practice shows, when developing an interface, you should still adhere to clarity and minimalism principles. But in parallel with this, it is necessary to add tooltips that explain to users how the application works.
There are other ways to simplify the interaction with the application, for example, save the history of actions, use the previously entered information to reduce the number of steps in the future.
№2: Ignorance Of Regulatory Specifications
Regulatory specifications like user data protection or FDA are secret ingredients to a successful healthcare application. Failing to meet these regulatory requirements can thwart its release on any renowned application platform. The laws concerning the handling of application user data are revised perpetually. It is eminent that you follow such changes closely as it can affect the development process.
№3: API Security Vulnerabilities
APIs define how apps can communicate with other apps and systems and are used for sharing information. Out of the 30 mHealth apps tested, 77% had hardcoded API keys, making them vulnerable to attacks that would allow the attacker to intercept data as it is exchanged. In some cases, those keys never expired, and 7% of the API keys belonged to third-party payment processors that strongly advised against hardcoding these private keys in plain text. Yet usernames and passwords had still been hardcoded.
Other Common Startups Mistakes You Can Avoid:
- Poor app usability
- Lack of feedback and involvement of clinicians and medical professionals during healthcare mobile application development
- Flawed business model and development without concrete app concept & purpose
- Mediocre understanding of the healthcare environment
- Failure to use user-friendly content and language
Your Technology Partner for Healthcare App Development
Understanding what patients want to see in a mobile app is one thing and developing a healthcare app to match higher expectations is entirely another game. With over ten years of providing software solutions and working on more than 400 projects, the Light IT team contributed vastly to the success of many companies. We help large enterprises, growing mid-level businesses, and ambitious startups to ship delightful applications and differentiate their businesses from extensive competition.
Conclusions
Ok, so what do these figures and estimations boil down to? It appears that there are tremendous business opportunities for healthcare app development, and individual healthcare providers or organizations invest in this area to improve the quality of services, increase operational efficiency and promote patients' self-management behaviors.
When evaluating potential technical partners, always check for relevant industry experience. Ask for their portfolio. Ask about their approach, and review pricing, knowledge, privacy, and data security. Meet the team that will work on your project to assess their experience, skills, and professionalism.
There are many nuances in the launch of mobile applications in the medical industry, and we hope that this article will come in handy when making decisions.





