The scope and importance of digital transformation inspired us to create a series of articles. Each of them is dedicated to the influence of digitalization on a particular industry, such as banking or healthcare. Here is another addition to this collection, and it focuses on digital transformation in insurance.
Causes of Digital Transformation in the Insurance Industry
Before examining the directions and features of digitalization in insurance, it is vital to understand its reasons. The essence of the industry is protecting people and companies against risks, and such an activity ironically involves many risks of its own. The world is having a hard time at the moment: the economic crisis, climate change, and resulting natural disasters, regular pandemics, to name a few examples. These calamities impact all industries, but insurance is among the most affected.
In addition to these forces, there are other factors that make industries, including the P&C insurance industry, change and adopt digital technologies.
- Technological progress. The advances of digital technologies are undisputable and offer many beneficial improvements over conventional methods. Faster communication, more computational power, more secure storage of information, and othe r advantages find numerous applications in insurance.
- More demanding clients. As life conditions change, the clients of insurance companies change too. They demand better service, more favorable terms, and other privileges. Otherwise, they may go to a rival company. Digital transformation helps in providing improved customer experience and targeting new and existing audiences more effectively.
- Higher competition. Both society and the government frown upon monopolies, so there are plenty of companies that offer insurance services. As more and more newcomers enter this market, their rivalry becomes more intense, and they try to get any competitive advantage and attract customers. Digital technologies are an effective way to achieve those goals.
- More strict legislation. The government revises and improves the regulatory norms that protect customers from fraud, personal data theft, low-quality services, and other potential dangers. Insurance companies must comply with several standards if they want to operate in this field.
As you can see, there are four major forces that drive digital transformation across all industries. In this aspect, insurance is no different from other business areas that are focused on providing services to customers.
Key aspects of digitalization in property and casualty insurance
We have already established that P&C (property and casualty) insurance is yet another industry that undergoes changes spurred by digitalization. The blending of the insurance business and digital technologies even gave rise to a new term “insurtech.”
The insurance industry depends heavily on obtaining data and using it for various predictions, risk calculations, etc. For this reason, it’s first and utmost need is data mining solutions combined with processing and analytical means presented by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Let us examine a few exemplary aspects of use for digital technologies in this area.
Wide range of personalized offers
Like many other industries that provide services, insurance collects and analyzes user-specific information for several reasons. The data gathering is mostly performed using the Internet of Things, but some other elaborate methods are also employed.
As one illustrative approach, scraping data from open profiles in social networks can give astonishing insights about a person’s habits and credibility. More importantly, personal information tells service providers what an individual wants and can provide patterns when different needs arise. This presents a valuable marketing opportunity to make a customized offer to a client at the most favorable moment. Such an offer is almost a sure shot, and a customer will gladly accept it in no time. This targeted approach saves costs on marketing and provides a much better experience for clients.
For example, if an AI system employed by an insurance company obtains data from an online marketplace that a person has recently bought a plane ticket, it would suggest a personalized offer customized for travelers. If this system learns that a person has booked a bed at a ski resort, it would suggest health insurance that covers related accidents. In broader terms, when AI algorithms recognize or predict any situations that may be covered by insurance, but the actual risk for this person is below a certain threshold, they would suggest a personalized offer as a response.
Precise risk analysis
Due to the specifics of the industry, insurance providers are incredibly interested in risk analysis and forecasting. They have to pay money when their clients encounter troubles, so companies seek ways to reduce their losses. Digitalization provides powerful tools for analytics and brings modeling and prediction to another level of effectiveness that is beyond human capabilities.

One digital technology is not enough to perform an accurate analysis that takes into account multiple evident and subtle factors. Such a complex task requires a well-adjusted combination of data mining, artificial intelligence, and machine learning technologies capable of handling Big Data.
Similar to the banking industry, minimizing risks also involves fraud detection. It is performed by using the aforementioned combination of digital technologies to run background checks on persons, detect potentially fraudulent patterns, etc. Digitalization also facilitates the creation of databases containing information on persons who were found guilty or reasonably suspected of committing fraud or other finance-related crimes. Such information serves as a “block list” to deny insurance services to impostors, cheaters, and other types of undesirable clients.
New types of insurance
The integration of smart devices and communication systems into various objects surrounding clients brought new business models for insurance providers. For example, digital technologies enabled the appearance of Usage-based insurance (UBI). This concept is sometimes referred to as “pay as you drive” (PAYD), and this name roughly explains the concept. It is a “personalized” type of vehicle insurance that takes into account several driving-related factors.
UBI uses a combination of hardware and software solutions to collect information during the use of a particular vehicle. This data includes distance, time, location, vehicle type, and other factors that are combined by a dedicated AI platform into a driver’s “history.” The required information may be obtained from an on-board computer, a driver’s cellphone with enabled geotargeting, or other sensors and GPS devices.
The main goal of usage-based insurance is offering better insurance terms for drivers with good histories that use safe roads, new or well-maintained vehicles, and do not spend too much time behind the wheel. It also plays an important social role by promoting safer and more responsible driving. These and other advantageous features made UBI one of the most promising directions of the insurance industry both globally and in the United States.
Improved customer support
In industries with high competition among companies, their clients constantly raise their demands regarding the quality of provided services and support. Another goal of the digital transformation in insurance is improving customer experience by providing quick consults, preferably in an extremely convenient way.
AI chatbots are the result of digital transformation that provide fast customer support and deal with basic queries. This way, they reduce the load on support managers and the waiting time for clients. In this industry, chatbots powered by AI and ML technologies are used to answer a wide range of insurance-related questions. They are readily available 24/7 on desktops or mobile devices, which is very convenient for customers who can get information whenever they need it.
This is especially useful in case of the insurance business in the United States because it attracts many service providers and even more clients. For example, according to the National Center for Health Statistics, about 88% of the adult population under 65 have medical insurance. 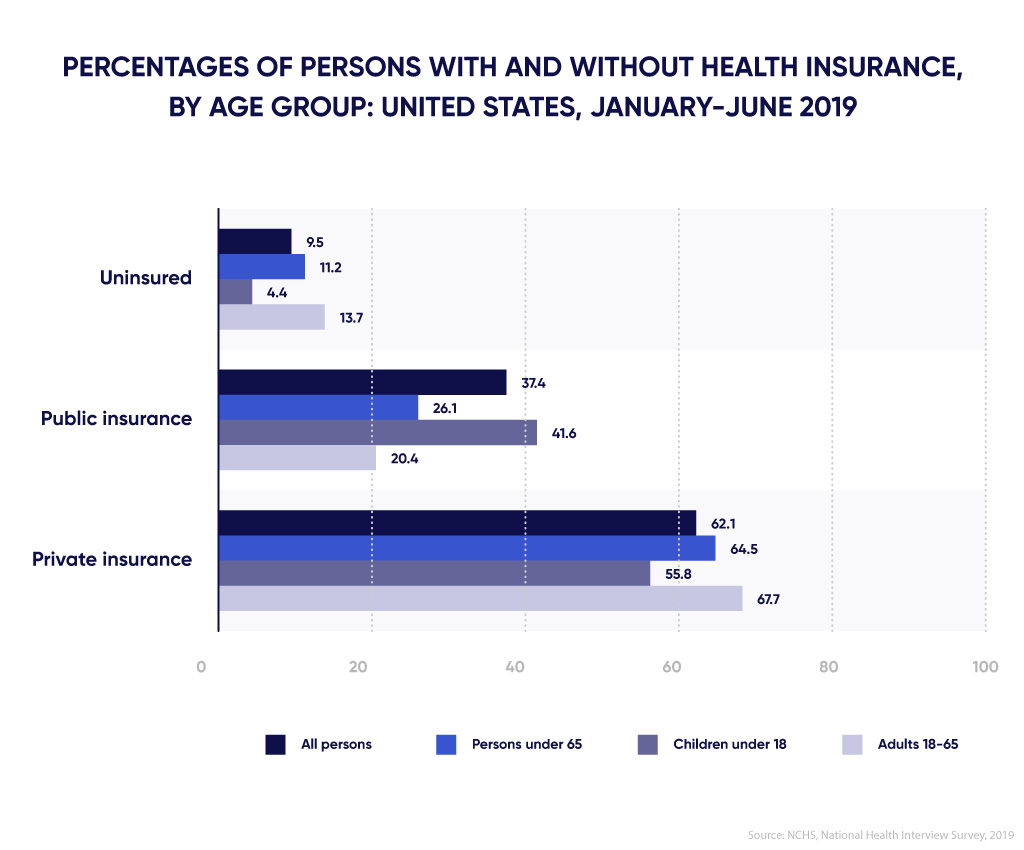
Challenges of Adopting Digital Transformation in Insurance
Despite the significant benefits provided to the insurance industry, the digital transformation (DT) also brings serious challenges. Here are a few examples:
DT requires an extremely cautious and well-planned approach
The digital transformation involves rebuilding an existing structure of the industry or a company, depending on the scale of implementation. It includes the majority of activities, methods, flows, etc. During this process, an insurance company or the whole system is vulnerable and unstable for a certain period of time before it gets accustomed to its new “transformed” state.
The key to a successful digital transformation is careful planning and developing a step-by-step strategy to cover all possible scenarios and complications in advance. This is especially true for insurance as well as other industries that deal with financial services and personal data. New technologies must be integrated seamlessly in order to provide improvements over existing approaches. Otherwise, the consequences in terms of money and reputation could be dire.
DT involves cybersecurity concerns
Converting data to the digital format, creating communication networks, and enabling easier access to information are among the primary goals of the digital transformation. However, they also have a major downside. Computer networks increase the possibility of information leaks, data tampering, and other attacks.
In order to prevent unauthorized access to their systems, insurance providers must implement a combination of security measures on hardware and software levels. These measures are not a one-time effort but rather an ongoing process of constant improvement. Hacker attacks become more elaborate and require more effective means to fend them off. This mutual evolution is the arms race of the digital era.
DT demands proper training
The digital transformation requires a collective effort of many experienced specialists. Moreover, it also requires computer-savvy staff capable of using newly adopted technologies with maximum efficiency. Proper training drains resources from a company as it requires a lot of time and money.
Most computer solutions implemented in the insurance industry have certain “foolproof” qualities as one of the safety measures. However, an employee who lacks the required knowledge may still be able to cause damage to the system without such an intent.
DT costs a lot
As you can see from the previous paragraphs, the digital transformation has high requirements. As such, they always involve high costs. Before an insurance company can enjoy the benefits of digitalization, it must prepare significant investments. Hardware, software, changes in infrastructure, implementation works, staff training – all these and multiple other processes drain money from a company. There are also other necessary and incidental expenses that result from temporary downtime periods, etc.
Conclusion
The digital transformation has already reshaped the insurance business and brought many improvements over the existing methods. As in any service-oriented industry, new technologies bring new ways of reaching and retaining clients. Digitalization also creates new insurance options that depend on the behavior and history of a particular customer. It also brings a new level of communication between a customer and an insurance provider.
The complexity of the digital transformation demands high-quality software, as well as skilled and responsible specialists. Contact us, and we will develop and implement custom solutions to add the benefits of digitalization to your insurance company




