Sometimes, when clients come to a software development company with just an idea of a web or mobile app, they do not understand the workflow and the necessity of certain stages. One of the frequent questions is “why do I need a mobile app prototype?” This article defines the concept of prototyping and describes the process and benefits of building a mobile app prototype.
What Is a Mobile App Prototype?
In the context of mobile software development, a prototype is an interactive but not yet functional draft of the future application. It shows the UI design, the user flow, and the planned functionality of the potential mobile app. For example, an iOS app prototype roughly shows how an application would look on screen resolutions of respective iPhone models.
Prototyping involves modelling the app UI design without actual coding and belongs to the pre-development stage. It may be performed as an integral part of the planning stage before mobile app development or as a separate service provided by software development companies. Since it is a rough draft, it may be done by a project manager without a design team.
Mobile app prototypes provide many benefits which will be described in more details later in this article. The most important of them is early testing an app concept to check its attractiveness for users. It is vital to test the viability of the initial idea in order to reduce the chances of future financial losses should the application fail to meet user demands. Statistics show that users uninstall 68% of mobile apps after trying them, and building a mobile application prototype increases the chances for your software to stay on user devices.
 Mobile app UI prototyping is generally performed using one of two distinctive approaches:
Mobile app UI prototyping is generally performed using one of two distinctive approaches:
- Throwaway or rapid prototyping. In this approach, the created prototype is not used after testing and obtaining software requirements. The core characteristic of such a method is the fast speed of building a model, testing it, defining the requirements and amending the initial concept.
- Evolutionary or breadboard prototyping. As the name suggests, in this approach, a prototype is the core of the future mobile application, and its functions are added subsequently. Over time, this model is improved to the point where it becomes the MVP and, eventually, the final version of the app. This approach does not allow defining the app requirements precisely or plan all the features before coding begins. However, through constant updating and refining, the prototype evolves into the intended final realization of the original vision.
What Is the Process of Making a Prototype of Your Mobile App?
Some development teams consider prototyping as one of the earliest stages in the app development workflow that precedes the programming stage, while others view it as a part of the planning stage – a precursor of the app development process. For this reason, it is better to describe the prototyping process not separately but in combination with the previous steps and in the scope of the app development workflow.
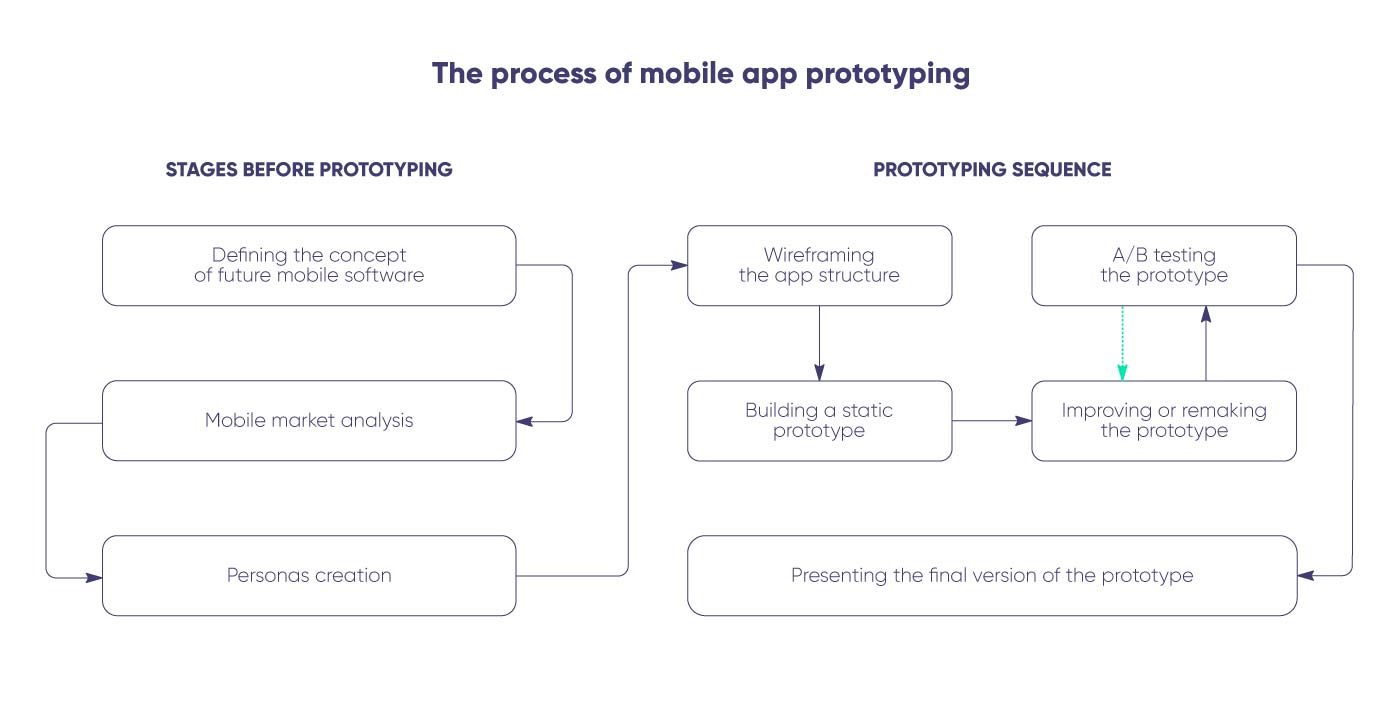
Stages before prototyping
The idea of a mobile application may be born under different conditions. It may be a spontaneous insight that appears during working routine, an epiphany triggered by a random image or action, or a planned result of a brainstorm.
That is why the first step before making a mobile app prototype is defining the concept of your future software. Our age may be digital, but nothing grasps the fleeting idea better than quick strokes of ink or graphite on paper. A scribbled list of features or doodles of the future app interface would be recreated and refined in the digital format on the later stages.
After you have captured the idea, you have a draft of your potential mobile app. Now, it’s time to start checking how good your concept really is. Hence, the next step is using the mobile market analysis to find out the current demand for your proposed software, the presence of competitive solutions, their advantages and flaws, and so on. It is vital for further development steps to prove that users will use your mobile application, so you will return your investments and make profits.
This step reveals whether the idea is bad from the start, or cannot compete with its market rivals, or the current technologies and staff availability cannot ensure the success of the application. Alternatively, the idea may be good, but the time to enter the market may be wrong, so the app should wait.
Another important step is creating relevant types of personas for subsequent testing. Personas represent the potential users of the future app with predicted behavior, preferences, and values.
Prototyping sequence
When your idea is proven to be financially promising and technologically feasible, it’s a green light to create a prototype for a mobile app based on the data gathered in the previous steps. The data includes technical specifications, a list of required features, any sketches or other drafts of the desired UI and the structure of the app.
The first step is wireframing the structure of your future app with the help of classic pen-and-paper sketching or directly using specialized digital tools. A wireframe is a barebone structure of the app with all the links and predicted user routes but without design elements.
The next step, building a static prototype, can be based on the results of the wireframing step or may be performed in parallel with it. The aim of this step is to set and show the transitions among app pages.
A/B testing the prototype involves sharing it with the group of experts or volunteering enthusiasts. Testers employ different personas that represent major audiences of mobile software users. This extensive step is essential for developing interactive prototypes of mobile software products. User testing helps designers to obtain usability-related data that answers such questions as:
- is the interface layout convenient to navigate?
- are the texts on UI elements easy to understand?
- can users perform intended actions effectively using the UI?
- are there any elements that disrupt the app functionality?
The results of usability tests are employed in the next stage in order to amend detected flaws. In its turn, the testing stage may be repeated until no more drawbacks are found in the UI.
Improving or remaking the prototype using the testers’ feedback is another crucial phase of prototyping. This stage is vital for ensuring intuitive and convenient operation and making the future mobile application more attractive to its target audience. After this step, the prototype returns to the testing stage, and the cycle continues until the satisfactory result is obtained.
Presenting the final version of the prototype may depend on the selected approach. The result of throwaway prototyping is discarded, while the outcome of evolutionary prototyping moves to the development stage where it is further upgraded.
Tools for Fast and Easy Prototyping
The true beauty of app prototyping is that you do not need a professional designer to build an interactive UI model. There are plenty of desktop software and online services that provide the ability to create both web and mobile app prototypes. Some of them are rather sophisticated and require time to master, while others are intuitive and simple, offering a “drag-and-drop” design process.
Several examples of popular prototyping tools include: Adobe XD, Sketch, InVision, proto.io, Fluid UI, UXPin, Marvel, Keynote, POP (prototyping on paper), Mockplus, and Balsamiq Wireframes. Thus, you can choose from multiple variants that greatly differ in price and can be installed on Windows, Mac, mobile devices or run in browsers.
Benefits of Mobile App Prototyping
Mobile application prototyping brings many advantages that facilitate further development in several ways. Below there are some illustrative examples of such benefits that show the importance of the prototyping process.
- Better definition and understanding of the mobile app concept. Prototyping brings more clarity to your initial vision that helps both developers and investors to fully realize the idea of the future mobile application.
- Improved user experience. Prototyping allows receiving user feedback before development begins, which is an invaluable source of data. Due to extensive testing and improving the app usability, the resulting mobile application will be more attractive to customers, which involves better profitability.
- More potential for drawing investments. The idea of an app embodied as an interactive prototype is more attractive and clear to potential investors than drawn flowcharts and sketches. This method requires less money and time in comparison with a functional MVP, so it can be presented faster to the interested parties.
- Better cooperation among designers, coders, and testers. Since prototyping involves steps of testing and optimization, it helps to coordinate the staff and facilitate their communication for further stages of software development. In its turn, predicted and coordinated workflow results in faster and cheaper development.
In combination, the listed advantages help to reduce development costs and time, decrease the possibility of sudden changes in the app structure and in the workflow, and otherwise facilitate the subsequent development stages.




