Healthcare is a constantly evolving field where technology drives many of the fundamental improvements in patient care, operational efficiency, and data management. One of the core technological pillars supporting these advancements is Health Level Seven (HL7), a widely used set of international standards that govern the exchange of electronic health information.
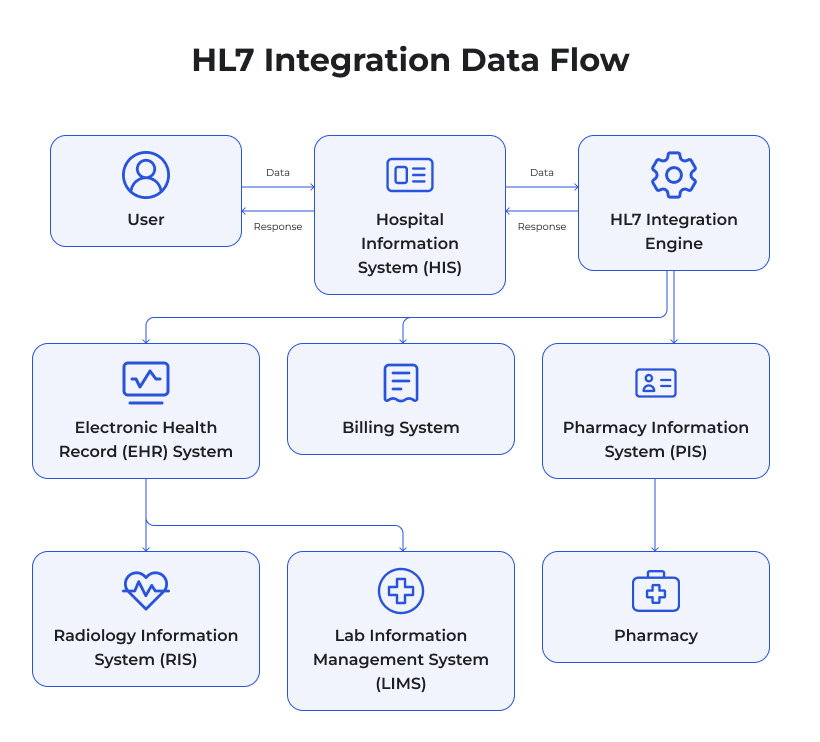
HL7 outlines the messaging and data structures used for seamless communication between various healthcare systems such as Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, laboratory information systems, billing and claims processing software, imaging platforms, and beyond. The ultimate goal of HL7 is to facilitate interoperability between the many different systems in a healthcare environment, enabling data to flow securely, quickly, and accurately among all relevant stakeholders.
HL7 plays a crucial role in helping medical facilities collect, store, and share standardized information, which reduces or even eliminates costly errors tied to manual data entry, misinterpretation of records, and delays in communication. In an industry where errors could have life-threatening implications, the need for robust, standardized data exchange cannot be overstated.
What’s The Point And The Purpose?
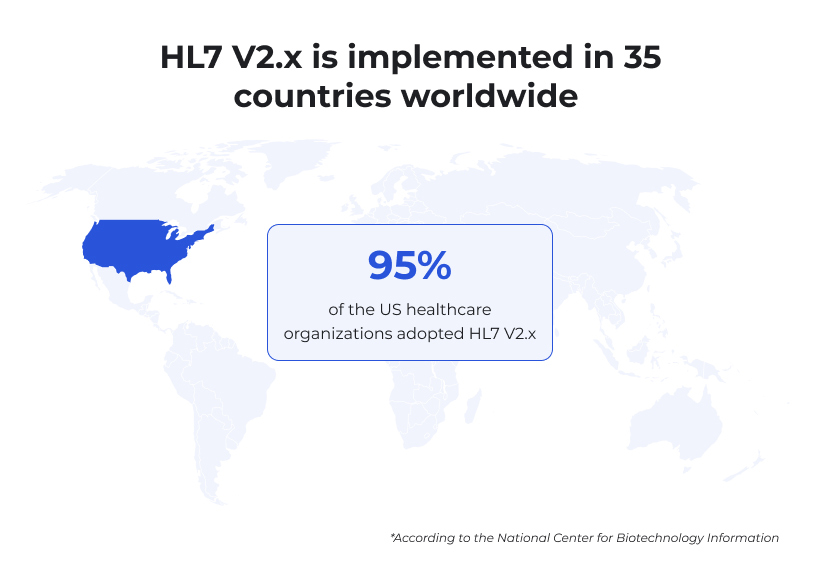
Healthcare providers often face a complicated array of software tools for different medical services, from diagnostic equipment to laboratory systems to clinical documentation. If these tools do not communicate effectively, it leads to information silos, redundant data entry, and potential inaccuracies in patient information. This can significantly compromise the quality and safety of patient care. HL7 integration is, therefore, critical for unifying data flows. By providing a framework for how different software applications should format and transfer health data, HL7 makes it possible for these siloed systems to operate as one interconnected ecosystem, drastically improving the overall continuity and efficiency of healthcare services. The efficiency is so evident that 95% of the medical facilities within the US alone have adopted HL7 V2.x and healthcare providers in 35 countries around the globe follow the same path.
HL7 integration is essentially the process of implementing HL7 standards within a healthcare organization’s information systems so that they can all “speak” the same language. By integrating HL7, healthcare facilities ensure that disparate systems, such as EHRs and lab systems, can share patient data accurately and in real time. The integration process often involves interface engines, data mapping, testing, and ongoing maintenance. When done correctly, HL7 integration becomes the bedrock for effective, interoperable operations, facilitating well-coordinated patient care, decreasing medical errors, and improving decision-making accuracy at both clinical and administrative levels.
By understanding and embracing HL7 integration, healthcare providers position themselves to offer high-quality services while lowering operational risks and costs. In this guide, we’ll explore the benefits of HL7 integration, break down the integration process, examine various approaches to HL7 implementation, highlight the most common challenges, and offer best practices for seamless integration. By the end, you’ll have a strong sense of how HL7 can revolutionize your organization’s data workflows and patient outcomes.
8 Most Prominent Benefits of HL7 Integration
HL7 integration is more than just a technical upgrade or software implementation. It’s a strategic step that empowers healthcare providers to streamline their workflows, produce more accurate patient records, and make better, more informed clinical decisions. Below are some of the key perks you as a business owner can expect upon HL7 integration.
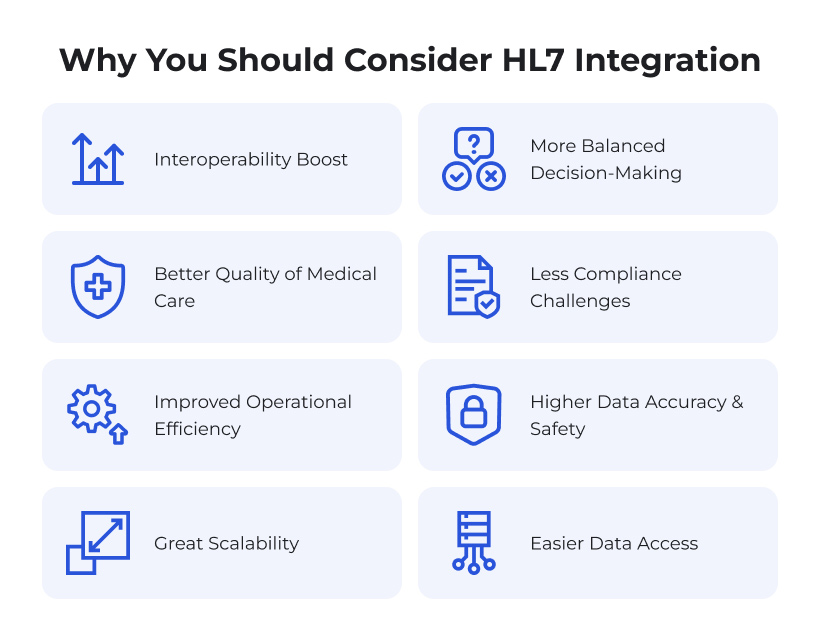
Interoperability Boost
One of the primary objectives of HL7 is to foster interoperability. In many healthcare settings, data is spread across multiple platforms. Some are dedicated to billing, others to lab tests or patient care documentation. Without a standardized method of data exchange, these systems struggle to share information swiftly and accurately. HL7 solves this problem by defining a standard format and protocol for electronic health data, which ensures that all connected systems can understand the transmitted information. This level of interoperability not only streamlines clinical tasks but also reduces the likelihood of data silos and redundancies.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Manual data entry has historically been a bottleneck for many healthcare providers, leading to an increased risk of errors and draining staff resources. HL7-based integrations can automate many data exchange tasks, such as transferring lab results from a laboratory information system into a patient’s electronic chart or electronically sending billing information to insurance payers. Such level of automation helps healthcare facilities reduce administrative burden, speed up overall workflows, and reallocate staff time to more patient-centric activities. Enhanced efficiency also helps cut operational costs in the long run, as fewer man-hours are spent on reconciling data inconsistencies.
Improved Patient Care and Outcomes
Every second can matter in healthcare, particularly during emergencies or when making critical care decisions. HL7 integration allows real-time exchange of patient data, giving clinicians access to up-to-date lab results, medication records, and treatment histories. This high level of data availability can lead to faster, more accurate diagnoses and treatments. Clinicians are better informed about patient allergies, medication conflicts, and recent test results, minimizing the chances of medical errors or duplicative tests. In addition, when interdisciplinary teams have ready access to the same standardized information, it fosters collaborative decision-making that ultimately improves patient outcomes.
More Balanced Decision-Making
In modern healthcare, data drives decision-making. When data is locked in different systems, capturing and analyzing it becomes complex and time-consuming. With HL7, decision-makers can rely on integrated data sets, making it easier to extract meaningful insights for both clinical and administrative purposes. This could involve identifying patient patterns, detecting potential resource optimization opportunities, or forecasting trends in patient admissions. With access to integrated data, leadership can make decisions that are both evidence-based and holistically informed, improving patient care quality and organizational performance.
Less Compliance Challenges
Healthcare providers often have to navigate a myriad of regulatory and compliance standards, from HIPAA in the United States to GDPR in Europe, and many others globally. By leveraging HL7’s standardized approach, organizations can more efficiently address specific compliance mandates around data exchange, patient privacy, and reporting. Although HL7 by itself does not ensure compliance, it offers a structure that aligns well with many regulatory requirements. This alignment can streamline audit processes and reduce the administrative load associated with maintaining compliance in areas such as data security, patient privacy, and record accuracy.
Higher Data Accuracy and Safety
Entering the same patient information in multiple systems increases the chance of typographical errors, duplication, or incomplete data capture. With HL7 integration, data is typically entered once and then distributed across the network of connected systems automatically. This reduces the duplication of data entry tasks, lessens the margin for error, and maintains a single source of truth for patient records. The consistency and reliability of data can have ripple effects across the entire organization, from improved research studies to smoother billing and reimbursement processes.
Great Scalability
As healthcare organizations grow, adding new services, locations, and patient populations, they need systems that can scale with them. HL7 integration is designed to be flexible; it can accommodate new data types, emerging technologies, and additional partners or third-party services. This modularity and expandability allow for incremental upgrades, letting healthcare providers adapt to rapid industry changes and expansions without overhauling their entire IT infrastructure. A facility that invests in HL7 integration today is better positioned to accommodate new healthcare applications, telemedicine solutions, or AI-powered analytics in the future.
Easier Data Access
In a healthcare ecosystem where HL7 integration is in place, data flows smoothly among different systems. This level of integration empowers physicians, nurses, administrative staff, and even patients (when patient portals are involved) to access the data they need with minimal delay. Centralized or unified data access isn’t just beneficial for the immediate clinical staff. It can also improve collaboration among specialists, enhance care coordination, and enable better patient engagement strategies. When data is more readily accessible, the entire care continuum benefits, resulting in superior clinical outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
Taken together, these benefits demonstrate the transformative potential of HL7 integration. By addressing critical issues like interoperability, data accuracy, and regulatory compliance, HL7 sets the stage for a more cohesive and efficient healthcare environment. Although achieving complete HL7 integration involves a series of technical and strategic steps, the return on investment (improved patient outcomes, operational efficiencies, and robust data management) is both immediate and long-lasting.
HL7 Integration Process Made Simple
The HL7 integration process is methodical, usually involving multiple teams, from clinical staff who define data requirements to IT professionals who design interfaces, map data, and maintain the system. While the exact pathway can vary between organizations depending on their existing IT infrastructure, resources, and goals, there are fundamental steps that every successful HL7 integration project follows.
Understanding the HL7 Standard and Its Versions
HL7, as an organization, has released multiple standards, each tailored to different healthcare communication needs. The most commonly used standard is HL7 v2.x, which is widely implemented worldwide for messaging between systems. HL7 v2 (and its successive updates) focuses primarily on the exchange of data in discrete messages, lab order and result messages, and billing messages. Although older, HL7 v2.x remains prominent because many legacy systems are built around it.
Another major standard is HL7 v3, which aims to be more comprehensive and consistent, relying on an XML-based framework. HL7 v3 includes the Clinical Document Architecture (CDA), used to create electronic documents like Continuity of Care Documents (CCDs) that can be shared across different platforms.
Additionally, there’s FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), which is the newest HL7 specification. FHIR leverages modern web standards (RESTful APIs, JSON, etc.) to make data exchange more agile, scalable, and user-friendly, particularly in mobile and cloud-based environments.
Understanding which HL7 version or combination suits your organization’s needs is one of the earliest and most critical decisions in the integration process.
Key Steps in HL7 Integration
Requirement Gathering
Before any technical work begins, it’s essential to understand the specific needs of the healthcare provider. Identify which systems must communicate with each other, the types of data they need to exchange, and the volume and frequency of these exchanges. This stage also involves determining use cases, such as lab results delivery, e-prescribing, or ADT messages.
Data Mapping
Data mapping is a crucial step for ensuring that the information from one system (e.g., an EHR) is accurately translated into a format recognizable by the receiving system (e.g., a billing solution). This involves identifying HL7 message types and segments and then defining how data elements from the source system correlate to data fields in the target system.
Interface Development
Once the mapping is clear, developers build the interfaces that will transfer the data. This could be done using a point-to-point setup, an interface engine, or other integration models (explored in the next section). The development process often includes configuring triggers (events that cause a message to be sent) and ensuring that each interface adheres to HL7 syntax and structure.
Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing is essential to confirm that messages are being sent and received accurately. Providers often conduct unit tests, system tests, and integration tests, followed by user acceptance testing. This phase may also include load testing to ensure the infrastructure can handle peak volumes without downtime or data loss.
Testing and validation ensure that data is not only transmitted but is transmitted correctly and securely. HL7 messages can be complex, containing numerous segments and data fields. A single mapping error can result in critical misinformation appearing in a patient’s record. Testing also verifies that workflows remain smooth, preventing disruptions in clinical and administrative tasks. Given the regulatory environment in healthcare, validation is indispensable for demonstrating compliance and building confidence among end-users.
Deployment and Training
After successful testing, the new HL7 interfaces and workflows are deployed to a production environment. Staff training is critical, as end-users need to understand all the new workflows, as well as how to identify and report potential integration errors.
Ongoing Maintenance
Post-implementation, HL7 interfaces must be regularly monitored for errors, performance metrics, and potential security risks. Healthcare providers often build a governance model that oversees updates, system expansions, and compliance checks. Because HL7 standards evolve, your interfaces may also need periodic updates to incorporate new segments or message structures.
Ultimately, the HL7 integration process should be approached as both a technological and organizational transformation. Proper planning, cross-functional communication, and iterative testing set the foundation for an efficient, reliable, and scalable HL7 environment that boosts interoperability and patient care.
Choosing the Right Type of HL7 Integration
When deciding how to implement HL7, healthcare providers can choose from several integration models, each differing in complexity, cost, scalability, and maintenance requirements. Selecting the right approach depends on your organization’s IT architecture, budget, and long-term strategy.
Below is an overview of the three primary types of HL7 integrations: point-to-point, interface engine-based, and cloud-based. We also discuss their pros and cons to help you make an informed decision.
Point-to-Point Integration
Point-to-point integration entails creating a direct link between two healthcare applications to exchange HL7 messages. This approach is often considered the simplest form of integration, especially if you have a small number of systems or specific use cases requiring minimal data sharing. A point-to-point connection uses customized interfaces or adapters that follow HL7 messaging protocols, ensuring data is properly formatted for each endpoint.
Benefits
- Simplicity: Developing a single interface for two systems can be straightforward and quick to implement.
- Cost-Effective (Initially): For small organizations or pilot projects, a point-to-point solution might require fewer upfront investments in specialized software or an interface engine.
- Direct Control: Having a dedicated connection allows for tight control over message specifications, versioning, and data transformations between the two endpoints.
Drawbacks
- Complex Scalability: As the number of connected systems grows, the number of point-to-point interfaces multiplies exponentially, leading to a “spaghetti” architecture that is difficult to manage.
- Maintenance Issues: Updating one system may require revisiting multiple connections, making version control and error resolution cumbersome.
- Limited Flexibility: Point-to-point integrations typically lack the advanced routing, filtering, and data manipulation features that more robust solutions provide.
A point-to-point approach might work for smaller clinics or organizations with a limited technology stack. However, for larger, more complex healthcare networks, it becomes unsustainable in the long run.
Interface Engine Integration
An interface engine serves as a central hub for exchanging HL7 messages between multiple systems, effectively acting as a communication “broker.” Instead of each system directly connecting to every other system, each system connects to the interface engine. The engine then manages message routing, transformation, and validation. Popular interface engines offer user-friendly dashboards, monitoring tools, and advanced features such as message queuing, error handling, and data normalization.
Benefits
- Scalability: Adding new systems or endpoints is more straightforward. You only need to create a single interface from the new system to the engine.
- Centralized Management: The engine offers a central point of control for all data flows, making troubleshooting, logging, and performance monitoring more efficient.
- Advanced Message Handling: Many interface engines can convert different HL7 versions or even non-HL7 data formats, enabling complex transformations.
- Lower Long-Term Costs: Although the initial investment might be higher, the simplified maintenance and adaptability can result in lower costs over time.
Drawbacks
- Higher Upfront Investment: Licenses and implementation costs for interface engines can be significant, particularly for smaller organizations.
- Learning Curve: Interface engines can be complex to configure and manage, requiring specialized expertise within your IT team or support from an external vendor.
- Dependency on Vendor: In some cases, you might become dependent on the vendor for updates, patches, or advanced features.
For medium to large healthcare systems or those anticipating rapid expansion, an interface engine is often the recommended approach due to its centralized control and long-term scalability.
Cloud-Based Integration
Cloud-based HL7 integration leverages Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms or Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) to manage your HL7 data exchange. Instead of installing and maintaining on-premise servers and interfaces, you connect your systems to a cloud service that handles message routing, transformation, and storage. These platforms often support modern web protocols and can integrate with an array of third-party services, including telemedicine apps, wearable device platforms, and population health tools.
Benefits
- Lower Maintenance Burden: The cloud provider manages software updates, security patches, and infrastructure scaling, minimizing the need for on-premise hardware and specialized personnel.
- Quick Deployment: You can often set up integrations rapidly thanks to pre-built connectors, templates, and APIs.
- Cost Scalability: Subscription-based pricing models allow you to pay for what you use, making it easier to scale up or down as business needs change.
- Access to Modern Protocols: Many cloud-based solutions natively support FHIR and RESTful APIs, aligning well with next-generation healthcare applications.
Drawbacks
- Potential Security Concerns: Although many cloud providers employ robust security measures, some organizations remain wary of storing sensitive patient data offsite. Regulatory compliance must be carefully scrutinized.
- Ongoing Operating Costs: While you can avoid large upfront investments, the subscription costs can accumulate over time.
- Dependency on Network Reliability: In a cloud model, you rely heavily on internet connectivity. Any network downtime can disrupt integrations.
Cloud-based HL7 integration is increasingly popular, especially for healthcare organizations looking for rapid deployment and modern capabilities like FHIR-based APIs. Still, regulatory compliance and reliable internet infrastructure remain critical factors in deciding if a cloud approach is right for you.
So Which One Is More Effective?
Cost: Point-to-point may seem cost-effective initially but can become expensive as you add more systems. Interface engines require a larger upfront investment but can be more economical in the long term. Cloud solutions often use a pay-as-you-go model but may increase operating expenses over time.
Scalability: Interface engines and cloud-based solutions are typically far more scalable than point-to-point integrations.
Maintenance: Point-to-point integrations are challenging to maintain once they proliferate. Interface engines centralize management, while cloud solutions outsource much of the maintenance to the service provider.
Vendor Lock-in: Interface engine and cloud solutions may create some level of dependence on specific vendors or platforms. Point-to-point integrations tie you to custom-built connections, which can be equally difficult to change without re-engineering your connections.
In a nutshell, the choice between these integration models depends on your organization’s strategic goals, IT capabilities, and budget. For short-term or smaller-scale projects, point-to-point might suffice. However, if you anticipate growth or require robust data exchange capabilities, investing in an interface engine or exploring cloud-based platforms may be the wiser, future-proof decision.
HL7 Integration Challenges You Should Know About
Despite its many benefits, HL7 integration is not without obstacles. From high costs to data governance to vendor lock-in, healthcare providers need to navigate a range of challenges to deploy HL7 systems successfully. Below are some of the most common obstacles you may encounter during the HL7 integration journey, along with strategies for mitigating each.

Relatively High Costs
Implementing HL7 integration can involve substantial upfront expenses, especially if you choose an interface engine or cloud-based integration. Licensing fees, software costs, infrastructure needs, and specialized personnel can add up quickly. Healthcare organizations with tight budgets or uncertain growth plans may find these costs daunting. However, consider the long-term return on investment, such as reduced manual errors, improved workflow efficiency, and lower compliance risks.
Some strategies for controlling costs include negotiating volume-based pricing with vendors, phased deployment, and leveraging grant funding when available.
Competency Challenges
HL7 integration requires a blend of clinical and technical expertise. IT professionals must understand the HL7 standards, message structures, and interface configuration, while clinicians need to define data requirements accurately. This creates a need for specialized training and cross-functional collaboration. Organizations might struggle to find or retain professionals who are well-versed in both HL7 standards and healthcare workflows.
To address this, consider creating cross-functional teams early in the process and providing ongoing training programs that equip your staff with the necessary HL7 and interoperability skills.
High Variability
HL7 is a standard, but it allows for customization to accommodate unique organizational needs. Hospitals, labs, and software vendors can implement HL7 in different ways, leading to variations that complicate integration. For instance, one system may use custom segments or define data fields differently. Handling these variations requires careful data mapping, robust testing, and continuous updates to accommodate new or updated vendor interfaces.
Ensuring alignment on HL7 implementation guides and maintaining clear documentation can help reduce the complexities arising from variability.
Maintenance Overhead
HL7 interfaces are not “set-and-forget.” They need regular updates, monitoring, and error resolution. As healthcare organizations evolve, adding new services, adopting new software, or modifying existing workflows, HL7 connections need to be recalibrated. Moreover, routine software patches, security fixes, and version upgrades can introduce unexpected hiccups into previously stable integrations.
Developing a strong governance model, including a dedicated integration team, can ensure that maintenance tasks are scheduled, tracked, and resolved promptly.
Data Quality and Validation Issues
If the data entering the integration pipeline is incomplete, outdated, or inaccurate, the HL7 interface will simply transmit those errors downstream. Bad data can lead to serious clinical and administrative errors, affecting patient safety and billing accuracy. Integrations that lack robust data validation and error-handling mechanisms can exacerbate this problem, as incorrect or malformed HL7 messages might go unnoticed.
Strategies to combat data quality issues include setting up real-time validation checks, implementing data normalization processes, and creating a culture of data accountability where errors are swiftly identified and rectified.
Limited Support for Modern Web Protocols
HL7 v2.x, the most widespread version, was developed in an era before modern web technologies. While HL7 v3 and FHIR provide more contemporary data exchange methods, many legacy systems still depend heavily on older protocols. This can hinder integration with emerging healthcare apps that rely on RESTful APIs or smartphone-based communications.
To bridge this gap, providers often rely on middleware solutions capable of translating HL7 v2.x messages into FHIR resources or vice versa. Investing in solutions that can handle both legacy and modern protocols is crucial for future-proofing.
Data Governance and Ownership
When multiple systems and departments share and modify the same patient records, questions arise around data ownership, stewardship, and accountability. Establishing robust data governance policies and clearly defining roles and responsibilities is imperative. These policies should outline data quality standards, define access rights, and describe escalation procedures for conflict resolution.

Vendor Lock-in Risks
Relying on a single vendor’s platform or integration engine can create a lock-in scenario where switching providers becomes expensive or operationally complex. This risk becomes more pronounced if the vendor uses proprietary message formats or custom HL7 extensions that are not easily transferrable.
Mitigation strategies include choosing vendors that adhere to open standards, negotiating contracts that include exit clauses, and maintaining your own HL7 expertise in-house to reduce dependence on any single vendor.
Successfully tackling these challenges paves the way for effective and sustainable HL7 integration. With a proactive strategy to address common pitfalls, your organization can fully leverage HL7 to deliver high-quality patient care in a digitally interconnected healthcare ecosystem.
Let’s Talk Best Practices
HL7 integration is a significant undertaking that can fundamentally transform the way healthcare data is managed and utilized. To maximize the benefits and minimize potential pitfalls, consider adopting the following best practices. While each organization’s journey will vary, these recommendations are broadly applicable and have proven valuable in numerous successful HL7 projects.
Importance of Proper Planning and Communication
- Project Scope and Requirements: Clearly define the scope of the HL7 integration project from the outset, listing which systems will be integrated, the type of data exchanged, the message frequency, and any compliance requirements.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage both technical and clinical stakeholders. Clinicians, administrators, and IT professionals each bring unique insights into data use cases, workflow needs, and limitations of existing systems.
- Regular Status Updates: Maintain open communication to discuss progress, challenges, and changes in scope. Weekly or bi-weekly status meetings can help identify and address integration issues early.
- Risk Management: Assess risks, such as potential downtime or data mismatches, and develop contingency plans. An early recognition of challenges helps in more effective risk mitigation.
Tips for Selecting the Right Integration Solution and Vendor
- Evaluate Scalability: Even if you currently have a small facility, healthcare needs can change rapidly. Look for solutions capable of handling growing data volumes and new functionalities, such as telehealth or AI-based diagnostics.
- Check Interoperability Features: Ensure the platform or vendor supports multiple HL7 versions, including FHIR for modern integrations. Look for advanced features like data mapping tools, message transformation, and real-time monitoring dashboards.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Weigh upfront costs (licensing, hardware, configuration) against ongoing expenses (maintenance, upgrades, vendor support). Request clear quotes from vendors and ask for references from existing clients.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: Investigate the vendor’s track record, user reviews, and case studies. Good vendors offer support, extensive documentation, and training materials.
- Security and Compliance: Verify that the solution can meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA, GDPR, or other regional data protection laws. Ensure that robust encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails are in place.
Best Practices for Ongoing Maintenance and Support
- Continuous Monitoring: Use monitoring tools and dashboards to track message flows, error rates, and system performance in real time. Early detection of issues prevents disruption to clinical workflows.
- Scheduled Updates and Testing: Plan for regular software patches and version upgrades. Always test new updates in a staging environment before deploying them to production to avoid unexpected downtime.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Maintain regular backups of configuration files, data mappings, and message logs. Implement a disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps to restore interfaces and data flows in case of a system failure.
- Performance Optimization: As data volumes grow, review interface performance and optimize processes like filtering unneeded segments or archiving old data to keep systems running smoothly.
- Documentation: Maintain up-to-date documentation detailing every interface, data mapping, and workflow change. Comprehensive documentation streamlines troubleshooting, onboarding new team members, and ensuring consistency across projects.
- Training and Capacity Building: Foster an environment of continuous learning. Encourage staff to attend HL7 conferences, webinars, or online courses. Cross-train multiple team members to avoid reliance on a single “HL7 guru.”
To Wrap It Up
Make no mistake, the future of HL7 integration is bright, particularly as FHIR gains traction in supporting modern web protocols and mobile applications. As telehealth, remote patient monitoring, and population health management become more integral to healthcare delivery, HL7 will play an ever-larger role in unifying data streams from multiple sources. This convergence of innovations promises a more patient-centered, data-rich ecosystem where care is informed by the most accurate and timely data available.
For healthcare providers aiming to thrive in this dynamic environment, investing in HL7 integration is no longer optional; it’s essential. By understanding the nuances of integration models, proactively addressing challenges, and following recognized best practices, you can establish a robust, scalable, and secure HL7 framework. It will help you not only meet today’s demands but also adapt to the breakthroughs of tomorrow, ultimately elevating the standard of care your organization can provide.
.



